EM waves that have different wavelengths can travel at the same speed, but their frequencies must also be different.
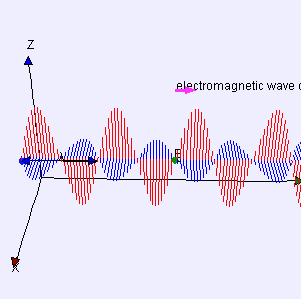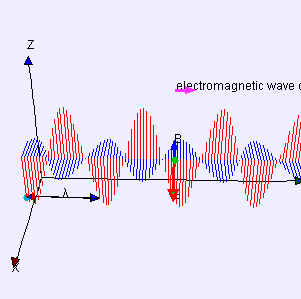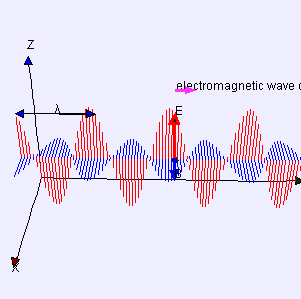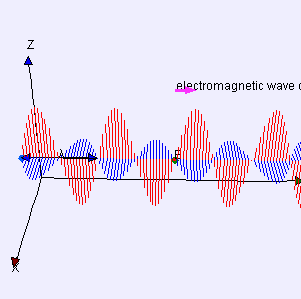
Radio waves and Microwaves
- Radio Waves
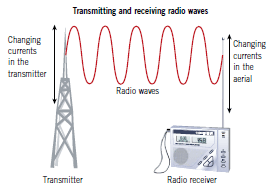
These waves cover a wide section of waves in the electromagnetic waves (EM) spectrum. Radio waves at most times have the longest wavelengths and the lowest frequencies of all types of EM waves. Any wavelength of an EM wave that is longer than 30 cm is considered a radio wave.
Radio waves are used foe broadcasting radio signals. Radio stations compute sound information into radio waves by differing the waves' amplitude or their frequencies.Changing amplitude or frequencies is called modulation.
There are AM and FM radio stations. AM stands for "amplitude modulation" and FM is "frequency modulation".
Television signals are also carried by radio waves.



- Microwaves
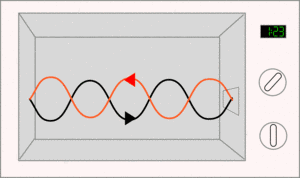
Microwaves have shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than radio waves do. You know when a wave is a microwave because their wavelength are between 1 mm and 30 cm. Microwaves are used to send information over long distances.
Microwaves are also used in radar. Radar (radio detection and ranging) is used to detect and see the speed and location of objects.
Infrared Waves
Microwaves are also used in radar. Radar (radio detection and ranging) is used to detect and see the speed and location of objects.

Infrared Waves
- Infrared Waves
The sun is one source of infrared waves. Our skin absorbs these waves when they strike our body (from the sun). The energy from these waves causes particles in our skin to vibrate more, which cause our temperature to rise.
The amount of infrared waves an object repels and gives off depends on the object's temperature. Warmer objects give off more infrared waves. While cooler objects give off less.
Infrared waves are not visible to us. But some devises detect these waves.

Visible Light and Ultraviolet Light
- Visible Light
Visible light is the very narrow range of wavelengths and frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum that us, humans, can see. Visible light waves have longer wavelengths and higher frequencies than infrared waves do. There wavelengths of these waves are between 400 nm and 700 nm.
Energy from the sun that reaches earth can be visible light. This visible light from the sun is white light. White light is visible light of all wavelengths added together.

- Ultraviolet Light
Some bad effects include sunburns. These types of waves can cause skin cancer, wrinkles, and damage to the eyes.
Some good effects include the killing of bacteria on food and surgical tools. Skin cells produce vitamin D when the skin is exposed to this light.
X rays and Gamma Rays
- X rays

- Gamma Rays

Ryann Cornelius
40/40 for this work!
ReplyDelete